low end tidal co2 sepsis
Therefore patients with severe sepsis may have an elevated respiratory rate with a low end-tidal CO2 reading. A low end-tidal CO2 may indicate poor perfusion hypovolemia or sepsis.

Evidence Supports Using End Tidal Carbon Dioxide To Detect Prehospital Sepsis Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News
End-tidal carbon dioxide ETco 2 monitoring provides valuable information about CO 2 production and clearance ventilation.

. In MAP group FR began when MAP at most 100 mmHg. End-tidal carbon dioxide is associated with lactate levels and mortality in emergency department patients with suspected sepsis. End tidal CO2 for sepsis alert.
Am J Emerg Med. Therefore correlation between the end tidal CO2 and an ABGVBG measurement is needed to confirm the diagnosis of hypocapnia. The results therefore suggest that in mechanically ventilated patients with severe postinduction hypotension ETco2 should be.
Additionally low end-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO 2 levels have been associated with lactic acidosis organ dysfunction and mortality in ED patients with suspected sepsis. Start date May 8. From a retrospective single-center case-control study comparing low end-tidal carbon dioxide ETco2 postinduction in hypotensive patients due to anaphylaxis compared to other causes a low ETco2 contributed to the diagnosis of anaphylaxis.
In this study the aim was to review the applications of end-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO2 monitoring in emergency department multiple databases were comprehensively searched with combination of following keywords. A study was undertaken to determine the pattern of end-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO2 changes during asphyxia-induced cardiac arrest in a pediatric canine model. Low EtCO2 with other signs of shock indicates poor systemic perfusion which can be caused by hypovolemia sepsis or dysrhythmias.
Discover the key facts in understanding this technology and its implications in clinical practice. Sabahov 3 M-T Guinnepain 6 S. Cardiac output and end-tidal carbon dioxide.
There is more than one version of this tool. Throughout the resuscitation end-tidal CO 2 was consistently in the 28-36 mmHg range during VFCPR. A low end-tidal CO2 may indicate poor perfusion hypovolemia or sepsis.
A low end-tidal CO2 may indicate poor perfusion hypovolemia or sepsis. In critical care End Tidal CO2 monitoring is used to assess adequacy of circulation to the lungs which provides clues about circulation to the rest of the body. End-tidal Carbon Dioxide Monitoring in Low Tidal Volume Ventilation ETCO2 The safety and scientific validity of this study is the.
To determine the use of end-tidal carbon dioxide etco2 as an end point of sepsis resuscitation. Theres a piece in the Orlando Sentinel about etco2 as a trigger for sepsis alerts. Although the normal range for CO2 should be between 35-45mmHg CO2 monitoring gives healthcare providers a lot more insight into what is going on with a patients condition.
Prehospital identification and initiation of therapy for severe sepsis may. At the end of an exhaled breathnormally 38mm Hg or 51. On the other hand a high CO2 reading may indicate airway narrowing airway obstruction or respiratory distress.
What does petco2 of. End-tidal CO2End-tidal CO2 EtCO2 is the partial pressure of CO2. There are Capnometers which display a numeric reading of the CO2 Waveform Capnography which creates a graph of the CO2 as well as certain aspects about how the patient is breathing and.
Hunter CL Silvestri S Dean M et al. Also called capnometry or capnography this noninvasive technique provides a breath-by-breath analysis and a continuous recording of ventilatory status. However this may also be caused by pulmonary dysfunction with an increase in dead space volume.
There are four groups in this study. End-tidal carbon dioxide is associated with lactate levels and mortality in emergency department patients with suspected sepsis. Cecal ligation and puncture CLP was used to cause severe sepsis in male SpragueDawley rats.
End Tidal CO2 monitoring is essential as it is the fastest indicator of ventilatory compromise. Three etco2 readings were taken during a 1-minute time frame at 0 3. Sham n 5 CLP n 10 end-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO 2 n 10 and mean arterial pressure MAP n 10In ETCO 2 group fluid resuscitation FR began when ETCO 2 at most 25 mmHg.
What does etco2 mean. New posts Search forums. This was a prospective observational single-center cohort study of emergency department patients receiving treatment for severe sepsis with a quantitative resuscitation protocol.
In fact its commonly called the ventilation vital sign. More Than Just a Number. Search titles only By.
Capnography the measurement of exhaled carbon dioxide CO2 has been gaining popularity in hospital critical care environments and more recently in the prehospital setting as well. Evidence suggests a persistently low ETco 2 value and a widened Paco 2-to-ETco 2 gradient during CPR are associated with poor outcomes. New posts New.
These waste products then accumulate in. Low EtCO 2 with other signs of shock indicates poor systemic perfusion which can be caused by hypovolemia sepsis or dysrhythmias. End tidal CO2 revealing a substantially low CO2 measurement also suggests hypocapnia eg etCO2.
It can also help the healthcare provider determine if the patient is being ventilated adequately. If a patient has a high CO2 reading on the CO2 monitoring. Why do we measure end tidal CO2.
To determine the utility of a prehospital sepsis screening protocol utilizing systemic inflammatory response syndrome SIRS criteria and end-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO2. Capnograph is an indispensable tool for monitoring metabolic and respiratory function. On the other hand a high CO2 reading may indicate airway narrowing.
We conducted a prospective cohort study among sepsis alerts activated by emergency medical services during a 12 month period after the initiation of a new sepsis screening protocol. We included randomized controlled trials cohort studies and case-control studies of adult cardiac. ETCO2 emergency department monitoring and critical.
Why is CO2 high in. ETCO2 emergency department monitoring and critical. A low end-tidal CO2 may indicate poor perfusion hypovolemia or sepsis.
End-Tidal CO2 monitors do exactly as the name implies they monitor CO2 in the air that we breathe out.

Pin On Educational Medical Diagrams

Evidence Supports Using End Tidal Carbon Dioxide To Detect Prehospital Sepsis Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News

Sepsis Management For The Nephrologist American Society Of Nephrology

The State Of Sepsis With Dr Karin Molander Sepsis Alliance Chair Elect Jvion

Sepsis Early Recognition And Treatment In Prehospital Setting Vital For Patient Outcomes Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News

Jems Using Etco2 To Detect Sepsis Youtube

Vasopressors Demystified An Overview Of The Physiology Of Vasopressors Including When To Start When To Use Periphera Icu Nursing Icu Icu Nurse Critical Care

Sepsis And Septic Shock Emergency Medicine Cases Em Cases Podcast

Two Hours Of In Vivo Lung Perfusion Improves Lung Function In Sepsis Induced Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Seminars In Thoracic And Cardiovascular Surgery

Caep Sepsis Treatment Checklist Download Table

Icu One Pager Icu Nurse Critical Care Icu Nursing Critical Care Nursing

Use End Tidal Carbon Dioxide To Diagnose Sepsis Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News

C Roc Curves For Predicting Severe Sepsis Auroc Area Under Receiver Download Scientific Diagram
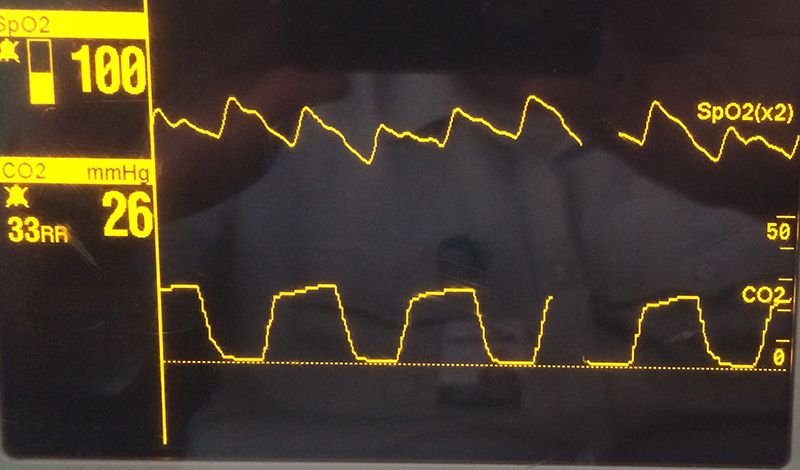
How Capnography Can Be Used To Identify Sepsis

End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Is Associated With Mortality And Lactate In Patients With Suspected Sepsis The American Journal Of Emergency Medicine

6 Useful Sepsis Assessment And Treatment Tips Capnoacademy Capnoacademy

